UWI-ARAD: Air Recirculation and Decontamination
At a Glance
-
PartnerMinistry of Health, Government of Trinidad and Tobago
-
Software LicenseThis project is under NDA and all software and output is proprietary.
-
Key Stakeholders
Primary Developer - Craig Ramlal; Medical Professionals.
-
Resources
Python – Node.js – Embedded Systems – Air Quality Sensors – Air Filters – UV Lamp – High-powered blower
-
Budget
The project was funded through the Government of Trinidad and Tobago's Research And Development Impact Fund: Hospitech: Supporting in-hospital COVID-19 response through technology.
-
Features• AdaptClean • Negative Zoning • Smart Placement (beta)
-
Proprietary Data and Software

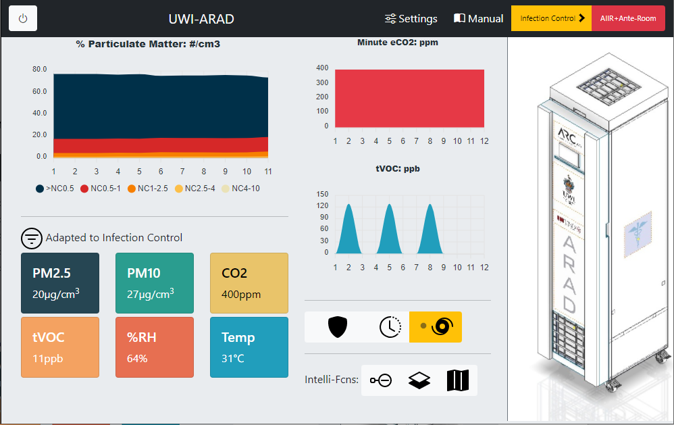
The UWI-ARAD system is a filtration and decontamination unit for medical spaces. The device aims to mix the room's air to minimize non-uniform spatial concentrations of particles via its high flow rate and the use of the Coanda effect. The device possesses smart technology that adapts its cleaning regiment, sets up negatively pressured isolation zones and features a 2-d computational fluid dynamic tool for optimal placement of the device in a contaminated/infected zone. The device is intended to be used in spaces that require either infection control, cleanrooms, negative differentially pressured zones or for general sanitization, filtration and air recirculation.
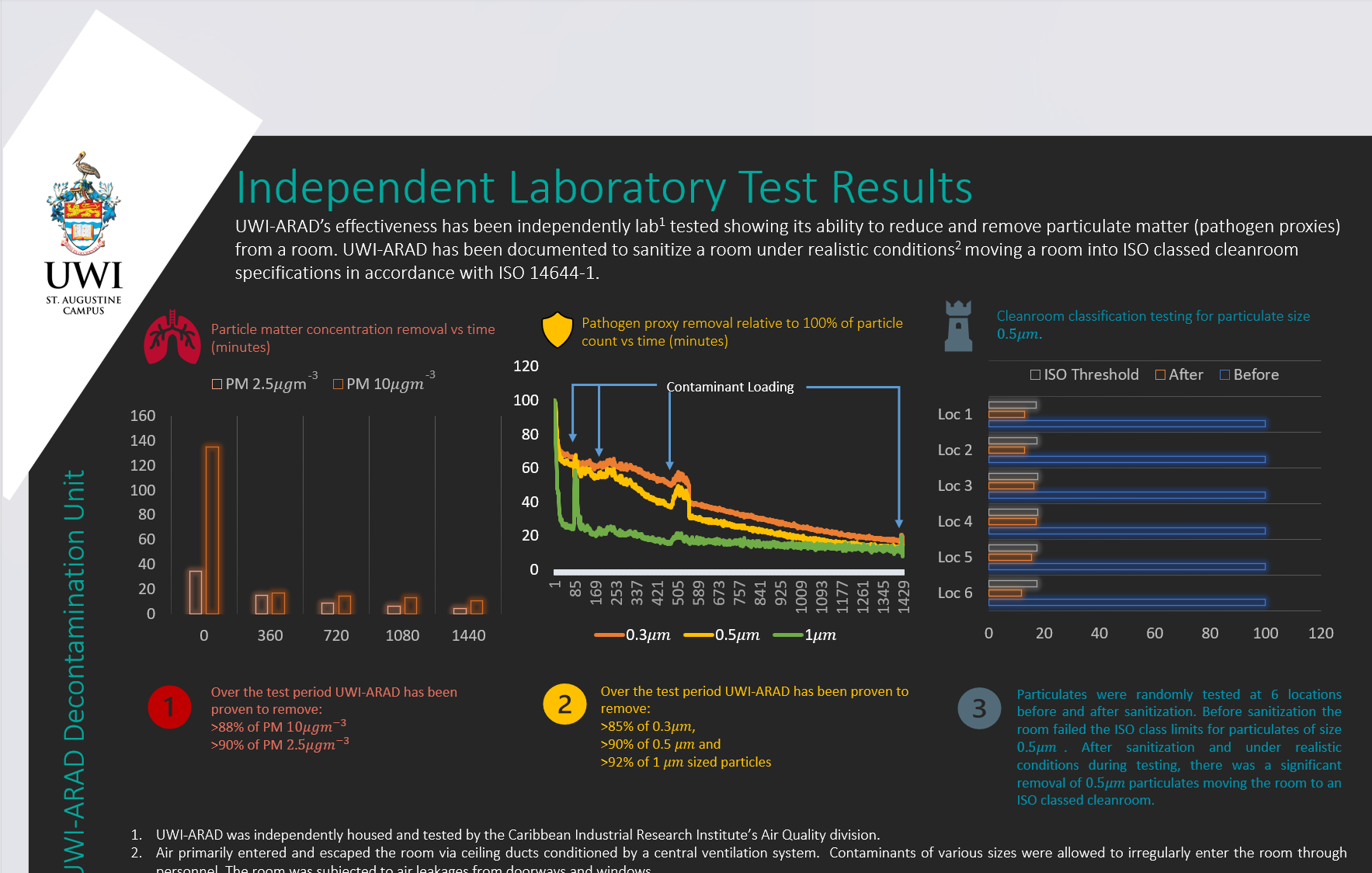
- AdaptClean: UWI-ARAD measures air quality indicators including particulate matter from PM 0.3 to PM 10, equivalent Carbon Dioxide (eCO2), total Volatile Organic Compounds (tVOC) and comfort indicators such as temperature and relative humidity. UWI-ARAD-Φ can isolate number count concentrations of ranges 0.5μm to 1μm and 2.5μm to 4μm, using these measures as proxies for respiratory droplets, if selected by the user. The device also monitors and tries to decrease PM2.5 and PM10 below limits specified by WHO, OSHA, IBN and ASHRAE Indoor Air Quality Guidelines.
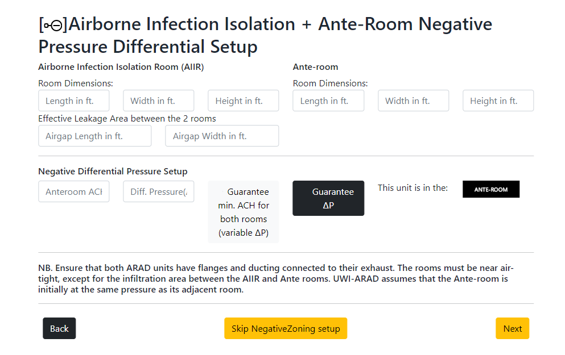
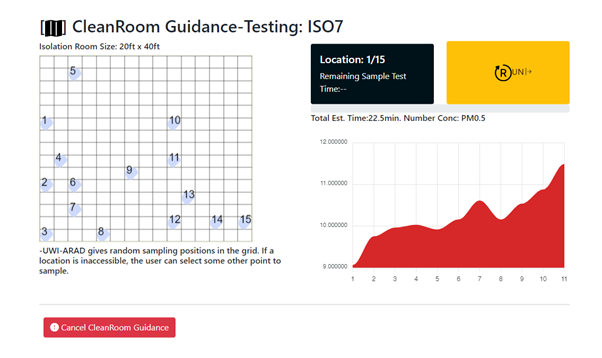
- Negative Zoning: is a tool that aids in setting up negative differential pressure zones. UWI-ARAD-Φ devices are placed within each zone and ducted to the outside. UWI-ARAD-Φ has continuous control over its airflow and with user selection of zone, differential pressure and ACH the device calculates the airflow automatically for each room and controls its flow output to the desired setting. The method remains the same for spaces with 2, 3 or 4 negative pressure differential zones. For large rooms, UWI-ARAD determines if multiple devices are needed. In summary negative zoning allows for UWI-ARAD-Φ to be configurable to the medical environments AIIR+anteroom and cleanroom needs.
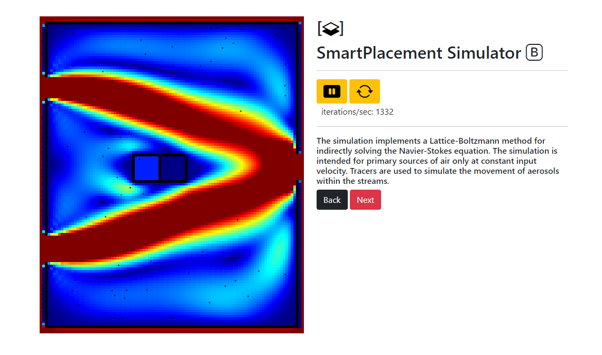
- Smart Placement (beta): The placement of a portable air cleaning device affects its efficacy and it is becoming prominent to use computational fluid dynamics as a means to justify the placement of an air purification unit. UWI-ARAD has a built-in computational fluid dynamics tool that implements the Lattice-Boltzmann method for indirectly solving the Navier-Stokes equation. The feature allows the user to construct air sources (eg. windows, ACs), sinks (eg. doorways, windows) and bodies (eg. Partitions, walls) within a room and simulate the transient and steady-state flows of the fluid with the movement of particles (viral particulate or otherwise). The device can then be located based on the highest concentration of particles.